Chemical Properties of Group 15 Elements
Chemical Properties of Group 15 Elements: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Chemical Properties of Group 15 Elements, Oxidation States of Group 15 Elements, Anomalous Properties of Nitrogen & Properties of Hydrides of Group 15 Elements etc.
Important Questions on Chemical Properties of Group 15 Elements
Match the following:
(i) The electron gain enthalpy of sulphur atom has a greater negative value than that of oxygen atom. (a) bond dissociation
(ii) Nitrogen does not form pentahalides. (b) small size
(iii) In aqueous solution HI is a stronger acid than HCl. (c) absence of d-orbitals
Which of the following statements are true:
(i) Phosphorus shows marked tendency for catenation but nitrogen shows little tendency for catenation.
(ii) The electron gain enthalpy with negative sign for oxygen is less than that for sulphur
A tetra-atomic molecule on reaction with Nitrogen (I)Oxide produces two substances (B) and . (B) acts as a dehydrating agent while substance is a diatomic gas which shows almost inert behavior. The substances and respectively are_______
The gases liberated when zinc reacts with dilute and conc. respectively are
In an organic compound phosphorus is estimated as
Which reaction (s) among the following produce Dinitrogen?
The acidic character of the group- elements in the increasing order is _____
The correct order for decreasing basic strength of the molecules , and is:
Which of the following is/are correct reason for the following statement: " has low boiling point than ".
Nitrogen does not form because
is basic while is:
Find the incorrect statement:
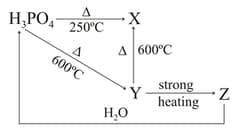 Identify :
Identify :
What is the oxidation state that is exhibited by group 15 elements when they react with metals?
Which of the following statements is wrong?
Which of the following elements does not show allotropy?
Bond dissociation enthalpy of bonds is given below. Which of the compounds will act as strongest reducing agent?
| Compound | ||||
The oxidation state of central atom in the anion of compound will be ______.
Maximum covalency of nitrogen is
exists but does not due to
